Vegetable Gardening in Small Spaces
Last Updated on December 28, 2022
How to Grow Vegetables in Small Spaces?
Designing a small vegetable garden is an excellent way to grow healthy vegetables, herbs, and fruits. A large garden bed for growing food in small spaces is unnecessary. You only need to choose the right type of soil and ensure the crucial necessities of plants. You can quickly enjoy organic vegetables in your small garden with the proper methods. Here are some tips for successful vegetable gardening in small spaces:
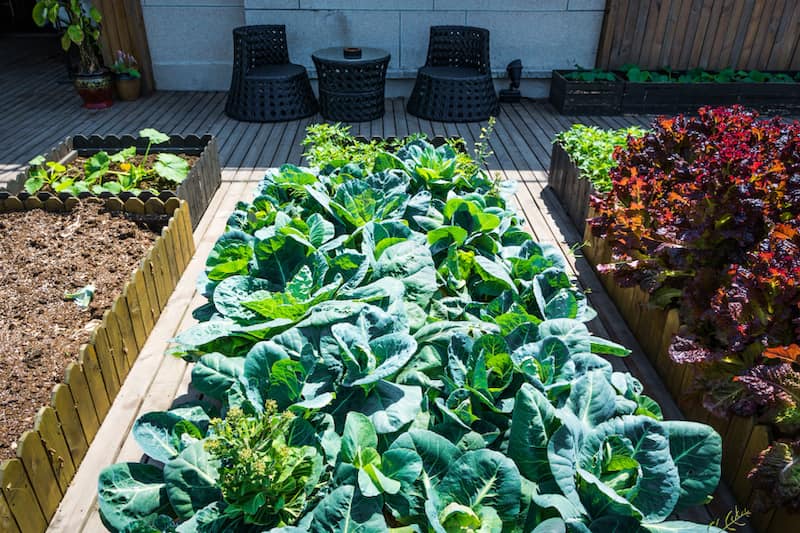

Choose the right vegetables: Some vegetables are better suited for small-space gardening than others. Some examples of small space-friendly vegetables include tomatoes, lettuce, peas, beans, radishes, and carrots.
Use containers: If you don’t have much space for a traditional garden, consider using containers such as pots, barrels, or raised beds. Just make sure the containers are large enough and have proper drainage.
Use vertical space: If you have limited horizontal space, consider using vertical space to grow your vegetables. This can be done by building or buying a vertical garden, trellising, or using hanging baskets.
Choose the right location: Make sure the location you choose gets enough sunlight for the vegetables you want to grow. Most vegetables need at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day.
Water regularly: All the plants need watering. Proper watering is important for the success of any garden. Make sure to water your vegetables regularly, but be careful not to overwater them. Therefore, you can install a simple irrigation system to water plants in your small vegetable garden. Here, you need to be careful not to have them plumped up suddenly. So, an irrigation system can help you water their roots properly. And you can save your vegetables from getting mildewed this way.
Fertilize as needed: Vegetables need nutrients to grow, so be sure to fertilize your plants as needed. You can use compost, fertilizer, or other organic matter to provide the necessary nutrients.
Pest control: Pests can be a problem for small space gardens, so be sure to keep an eye out for any signs of infestation and take appropriate action if necessary.
How to Plan a Small Garden Layout?
Planning a small garden layout can be a fun and rewarding experience. There are some essential elements of small vegetable garden layout plans and spacing. First, you need a sunny spot, such as a balcony, patio, or kitchen garden, to support the garden. Here are some steps to help you plan a small garden layout:

Determine the size and shape of your space: The first step in planning a small garden layout is to determine the size and shape of the area you have to work with. This will help you decide which vegetables and other plants will fit in your space.
In addition, you can do square-foot gardening while planning the layout of your garden to have a practical vegetable garden. It is designed in 4 by 4 feet squares with a grid and has 16 squares. You can plant different vegetables in each square. And the number of plants that you place in a square can change depending on the size of the plant. For example, if you have a single tomato plant in a square, you can plant four lettuces in the next. Also, when you receive the harvest, you can grow different vegetables.
Consider the sun: Most vegetables need at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day, so it’s important to choose a location that gets plenty of suns. Make sure to consider the direction of the sun when planning your garden layout. If vegetables and fruits do not receive enough sun, they cannot ripen.
Choose your vegetables: Decide which vegetables you want to grow in your small garden. Consider the size, growth habit, and sun requirements of each vegetable. Some vegetables, such as tomatoes and peppers, take up more space and may not be suitable for a small garden.
Plan for proper drainage: Good drainage is essential for a successful garden. Consider using raised beds or containers to grow your vegetables if your soil doesn’t drain well.
Make a sketch: Once you have a general idea of what you want to grow and where to make a sketch of your garden layout. This will help you visualize your plan and make necessary changes before planting.
Plant in blocks or rows: Planting in blocks or rows will make it easier to care for your garden and will also make it more attractive. Consider using trellises or other vertical growing structures to maximize space.
Add compost: Compost is an excellent way to enrich your soil and provide the necessary nutrients for your vegetables to grow. Make sure to add a layer of compost to your garden before planting. You can read “How to Make Organic Compost at Home?” for more info.
By following these steps, you can create a successful small garden layout that is both functional and attractive.
How to Maximize a Small Vegetable Garden?
It is crucial to determine the right spot for sunlight and provide essential elements to maximize the harvest in your small vegetable garden. In addition, here are some tips for gardening in small spaces:
Growing in Containers
Growing vegetables in containers make growing easier for some plants and pest management less complicated for you. Tomatoes, peppers, parsley, spinach, eggplant, radishes, cucumber, green onions, squash, lettuce, and beans are suitable to grow in containers.
You can use wooden boxes, bushel baskets, drums, gallon cans, and plastic or metal cans. Regardless of the container material, you need to drain it. It will improve drainage if a layer of coarse gravel is added to the bottom of the container.
Here, the size of the container matters. For example, 6 to 10 inches containers are appropriate for green onions and parsley. You can choose a smaller container for lettuce and radish.
Grow in Raised Beds
The depth of raised beds should be at least eight to twelve inches to give roots enough room to spread and grow. You need to fill the bed with fertile soil to achieve an environment to plant vegetables. Raised beds enable you to grow vegetables anywhere you think is available.
Also, they allow you to harvest more food by using less space. In raised beds, the soil warms up more quickly. You can choose the soil type and even blend it with fresh soil. Moreover, raised beds to make pest problems controllable and leave less room for weeds in your small vegetable garden.
Grow Vertically
When you plan your garden layout vertically, you need to consider the factors of wind, sun, and plant size to maintain your garden. You should support your vertical vegetable garden with aches, trellises, or tripods. And it would help if you remembered to consider the weight of a mature plant.
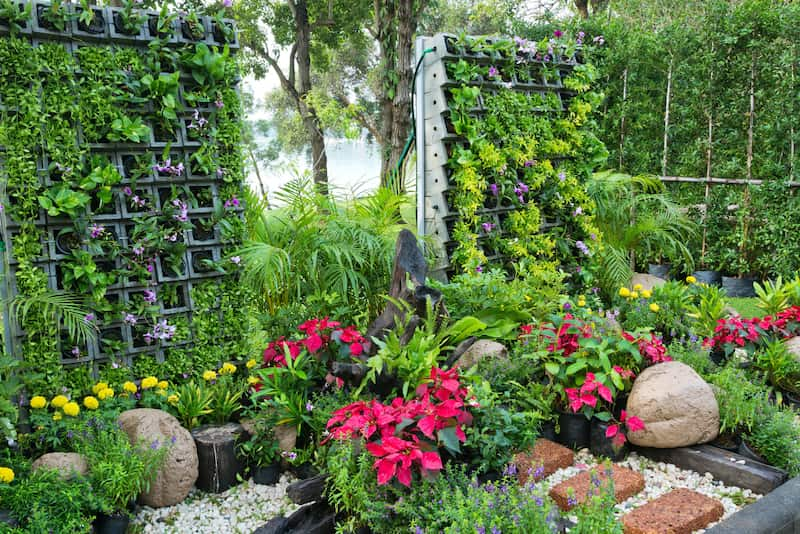

You can grow pole beans, green beans, climbing peas, sweet potatoes, cherry tomatoes, zucchini, cucumber, melon, and squash vertically. Growing more food in a small field, the easy harvest of vegetables and use of fertilizer, and reducing the possibility of diseases are the advantages of growing vegetables in this way.
Inter Planting
Interplanting requires pairing short plants with long ones so that short plants can grow under the tall ones. If this type of planting is completed successfully, it prevents diseases and makes it easy to control pests. This method is helpful if you have limited space in your small vegetable garden. However, you must ensure that the crops you are planting together need similar amounts of sunlight, water, and soil.
What Do Vegetables grow in a Small Garden?
If you like growing your fruits and vegetables, edible gardening, with its wide range of products, is just for you. You can plan your small vegetable garden regardless of the size of your garden’s space if you choose the right method for edible gardening in small spaces.
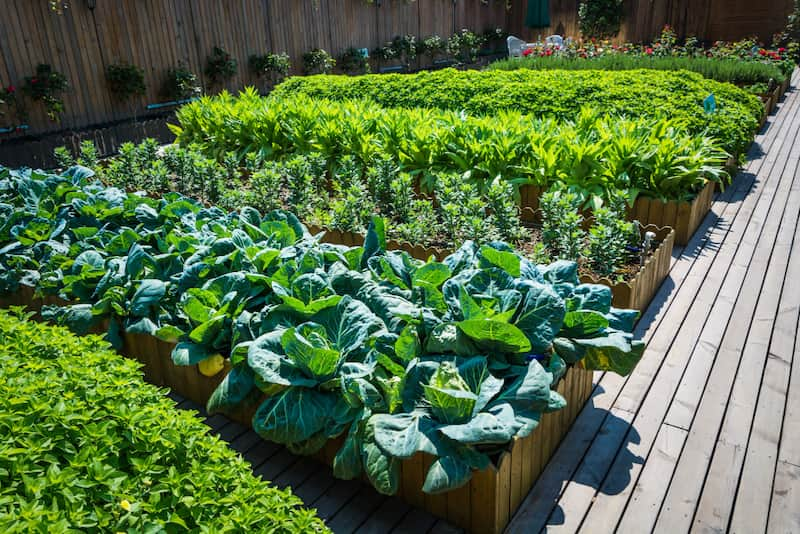

Many vegetables can be grown in a small garden. Some examples of small space-friendly vegetables include:
Tomatoes: Tomatoes can be grown in pots, hanging baskets, or raised beds. Just make sure the container is large enough and has proper drainage.
Lettuce: Lettuce is a fast-growing, cool-season vegetable that can be grown in pots, raised beds, or in the ground.
Peas: Peas are cool-season vegetables that can be grown in pots or raised beds. They can also be grown vertically on a trellis or other support.
Beans: Beans are another fast-growing, space-efficient vegetable that can be grown in pots, raised beds, or in the ground.
Radishes: Radishes are small, fast-growing vegetables that can be grown in pots, raised beds, or in the ground.
Carrots: Carrots can be grown in pots or raised beds as long as the soil is deep enough to accommodate their long roots.
Greens: Greens such as spinach, kale, and arugula are quick-growing, space-efficient vegetables that can be grown in pots or raised beds.
In addition to the vegetables mentioned above, peppers, basil, strawberry, shallots, parsley, flageolet bean, cucumber, black-eyed pea, zucchini, garlic, radish, shallots, early potatoes, broccoli, herbs, and courgettes are of the vegetables you can grow in your small garden.
How to Prepare Soil for Planting Vegetables in Pots?
Preparing soil for planting vegetables in pots is an important step in ensuring a successful harvest. Here are some tips for preparing the soil for planting vegetables in pots:
Choose the right soil: It’s important to use good-quality potting soil for planting vegetables in pots. Potting soil is specially formulated to provide the necessary nutrients and drainage for container gardening.
Add compost: You can produce your organic compost at home or buy commercial ones to spread on the surface to enrich the soil. Adding compost to your potting soil can help enrich the soil and provide the necessary nutrients for your vegetables to grow.
Check the pH: Your soil’s pH can affect your plants’ health. Vegetables have different pH preferences, so it’s important to check the pH of your soil and adjust it as needed. You can do this using a pH testing kit.
Aerate the soil: Aerating the soil helps to improve drainage and prevent compaction. You can use a fork or hand trowel to gently loosen the soil before planting.
Fertilize: Vegetables need nutrients to grow, so be sure to fertilize your plants as needed. You can use a slow-release fertilizer or apply a liquid fertilizer every few weeks.
By following these steps, you can prepare your soil for planting vegetables in pots and give your plants the best chance for success.
How To Reach or Sell Locally Grown Fresh Food?
UrbanicFarm has a revolutionary way to reach locally grown, fresh food. We connect micro gardening producers to the local distribution network across the country. Using the UrbanicFarm mobile app or website, local farmers, home gardeners, and micro farmers connect directly with consumers in their area –and lower freight costs.
To build a new foundation for a streamlined fresh food supply chain and social network, UrbanicFarm registers Gardeners–micro farmers and local farms with produce to sell and Consumers who want fresh, garden-direct food. We provide a map of their area updated with the locations and offerings of fresh local produce. If you have a fruit tree, extra produce from your garden, or other food you won’t use, you can offer them free, for sale, or for trade. Many home gardeners offer extra tomatoes, zucchini, and cucumbers from their gardens. Many trades for oranges, lemons, and apples. These are great ways for communities to collaborate and reduce food waste!
FAQs About Vegetable Gardening in Small Spaces
What Vegetable Is Easiest to Grow in Small Spaces?
Several vegetables are easy to grow in small-space gardening, including Lettuce, radishes, carrots, tomatoes, peppers, beans, zucchini, and eggplants.
What Vegetables Should Not Be Planted Together in Small Spaces?
While it’s possible to grow a variety of vegetables in a small space, some vegetables should not be planted together due to conflicting growing requirements or potential negative interactions. Here are some examples of vegetables that should not be planted together in a small space:
Tomatoes and corn: Tomatoes and corn should not be planted together because they have competing nutrient requirements. Tomatoes prefer a more acidic soil, while corn prefers a more alkaline soil.
Garlic and onions: Garlic and onions should not be planted near each other because they can both be prone to pests and diseases. Planting them together may increase the risk of these problems.
Carrots and dill: Carrots and dill should not be planted together because dill can interfere with the growth of carrots.
Cabbage and tomatoes: Cabbage and tomatoes should not be planted together because cabbage is prone to pests and diseases that can also affect tomatoes.
Beans and onions: Beans and onions should not be planted together because onions can inhibit the growth of beans.
By avoiding planting these vegetables together, you can help ensure the success of your small garden.
Should I Put a Fence Around My Small Vegetable Garden?
Fencing your garden helps you keep local animals out of your garden and protect your vegetables. You can also save your plants from the wind by choosing a fence that fits the style of your garden. A fence can also add visual appeal to your garden and help define the space.


Leave feedback about this